This Page is Home![]() Updates
Updates
What's New
Penta-Ocean Construction Co., Ltd.
Takuzo Shimizu, President, CEO and Representative Director
Development of AI-based Technology to Evaluate Residual Structural Performance of Piers
Tokyo, Japan – May 10, 2022 –Penta-Ocean Construction Co., Ltd., in collaboration with Professor Mitsuyasu Iwanami of Tokyo Institute of Technology, has developed a technology for evaluating the residual structural performance of piers using artificial intelligence (AI).
The harbor structures are subject to harsh marine environments including salt damage, and there are areas where some chloride-induced corrosion and other wear and tear damages cannot be visually checked, such as underwater areas and the underside of piers. For this reason, maintenance of harbor facilities is often performed in a "corrective maintenance" type of approach, where repair and renewal measures are taken only after a failure has occurred. However, from the standpoint of national resilience and sustenance and development of the economy, a shift to a "preventive maintenance” type of approach has recently been required.
This technology uses AI to predict how piers in harbors will be damaged by earthquakes and aging degradation, and provides indicators that can rationally determine whether or not a pier can continue to be used, the remaining service life, and the scope and timing for repair and renewal. The technology will thus help to promote the widespread application of a "preventive maintenance” management.
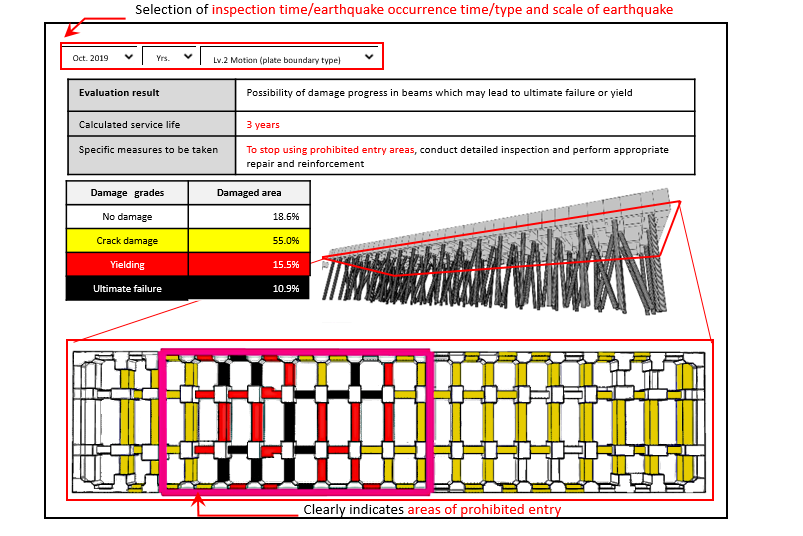
Generally, a pier consists of steel pipe piles, RC beams and slabs, and its service life usually depends on the corrosion of the rebar inside the beams. Therefore, we conducted structural tests on several specimens of beams with stepwise corrosion of rebar to clarify the relationship between the degree of deterioration and the bearing capacity of beams. As a result, we developed a structural analysis program that can evaluate each beam member in four stages: "no damage," "crack damage," "damage to yield," and "damage to ultimate failure”.
Furthermore, by learning over 2,000 combinations of input parameters such as the degree of deterioration of the pier, water depth of the site, diameter/number of piles and seismic ground motion, in addition to damage results from structural analysis, this new AI model is capable of evaluating the residual structural performance of the pier. The model predicts not only damages which may be caused by earthquakes, but also the progress of aging deterioration, making it possible to evaluate secular changes in residual structural performance over time.
With this technology, the facility managers can assess structural stability, the period of service availability, and specific actions to be taken at present by changing settings, such as the magnitude of earthquake and its time of occurrence. Moreover, in case repairs are carried out, conditions such as the scope and timing of repairs can be additionally set, allowing maintenance and renewal plans to be formulated with a view to life cycle costs.
Features
(1) Capable of predicting damage due to level 1 seismic ground motion*1 and level 2 seismic ground motion*2
(2) For the level 2 seismic ground motion, the following two earthquake types can be selected;
-Plate boundary type of earthquakes: Earthquake type similar to the Great East Japan Earthquake
-Inland epicentral earthquakes: Earthquakes type similar to the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake
(3) Capable of calculating the period of service life of a pier
(4) Capable of proposing specific measures to be taken immediately, such as the scope of prohibited entry.
*1 Level 1 seismic ground motion: Seismic ground motion that the facility is likely to sustain at least once during its design service period.
*2 Level 2 seismic ground motion: The largest seismic ground motion that can be expected to occur at the facility location.
System screen for residual structural performance evaluation technology