This Page is Home![]() Updates
Updates
What's New
Penta-Ocean Construction Co., Ltd.
Permanent Soil Cement Mixing Pile II (PSP II) Method achieves a 10% reduction in construction period and 10% cost saving for foundation work – Revised Building Technology Performance Certificate
On March 25, 2020, the nine companies formed by Asunaro Aoki Construction Co., Ltd., Hazama Ando Corporation, Okumura Corporation, Konoike Construction Co., Ltd., Penta-Ocean Construction Co., Ltd., Tekken Corporation, Toda Corporation, Nishimatsu Construction Co., Ltd., and MATSUMURA-GUMI Corporation, have revised the Construction Technology Performance Certificate of the General Building Research Corporation of Japan for the Permanent Soil Cement Mixing Pile (PSP) Method, which was jointly developed in 2003. The method is renamed “PSP II Method” after revision.
With this revision, in addition to the case where the indentation load acts on the PSP foundation (the structure in which the steel beam is inserted into the soil cement improved foundation) constantly or during earthquak we successfully enhanced the scope of application by establishing the appropriate design and construction method for the buildings where the pull-out load acts at the time of an earthquake.
1.Development background
Conventionally, the soil cement wall*1 was only used as a temporary earth retaining wall on the outer peripheral part of the building during underground excavation work, and additional piles were always required to support the building. However, if the wall can be used as a permanent structure, it will be possible to reduce the construction materials by cutting down the number of piles in the periphery portion.
Therefore, the nine joint development companies developed the PSP Method in 2003 to improve the performance of the soil cement wall for use as a ground improvement foundation for the permanent structure, acquired the Construction Technology Performance Certificate and promoted its application.
On the other hand, even for the buildings that can be directly supported by the basic foundation against indentation loads, there are cases of middle-to-low-rise buildings with large towering ratios where large pull-out loads act on the foundation during an earthquake. In these cases, the resistance force against the pull-out load is applied by constructing a permanent ground anchor or by excavating deeper to place thicker concrete foundation to increase the weight, both of which can act as pull-out resistance. In some of these cases where PSP Method is applicable, construction material was successfully reduced. However, due to lack of insight about the pull-out resistance of the PSP foundation, detailed review was required for individual cases, and consequently the personnel was forced to put significant effort to design works.
2.Technology outline
This method is a technology used to improve the performance of soil cement wall to utilize it as a permanent structure by ensuring a strict construction management and quality control.
We construct the improved soil cement foundation*2 which satisfies the required performance standard by stirring and mixing while injecting cement slurry into the foundation at the specified drilling speed and stirring frequency . Subsequently, the steel beam is then inserted into the foundation to transmit the building load (Figure 1).
After the indentation load of the building is transmitted to the steel beam, it is conveyed to the soil cement by the adhesive force between the soil cement and the steel beam, as well as through the resistance of the shear connectors (headed studs) placed at the tip, and then to the soil cement surface or the ground around the tip. On the other hand, after the pull-out load of the building is transmitted to the steel beam, it is conveyed to the soil cement due to the adhesive force between the soil cement and the steel beam, and then to the surrounding ground(Figure 2).
3. Verification of the technology
We conducted a pull-out test on a full-scale PSP foundation with a 650 mm diameter and confirmed its satisfactory structural performance against the pull-out load at the time of an earthquake. We also carried out a construction test on the improved soil cement and confirmed that the specified level of quality could be ensured for the required specifications, such as homogeneity and strength of soil cement, when the pull-out load is applied (Picture 1). From these results, in addition to the conventional design against the indentation load, we established the design and construction methods in order for it to withstand the pull-out load as well. Accordingly, we have revised the Construction Technology Performance Certification issued by the General Building Research Corporation of Japan.
When the method is applied to a 9-floor building with 1 basement floor, where the pull-out load occurs during an earthquake, the construction period will be shortened by 10% compared to the method of installing ground anchors to resist the pull-out load during an earthquake, and the cost was reduced by10%.
4.Future development
The nine joint development companies plan to apply this construction method to actual properties in order to further rationalize the foundation work and reduce the environmental impact.
*1 Soil cement wall
Soil cement in a columnar or continuous wall shape for use as a temporary earth retaining wall
*2 Improved soil cement
Soil cement with improved performance for use as a permanent structure in a columnar or continuous wall shape
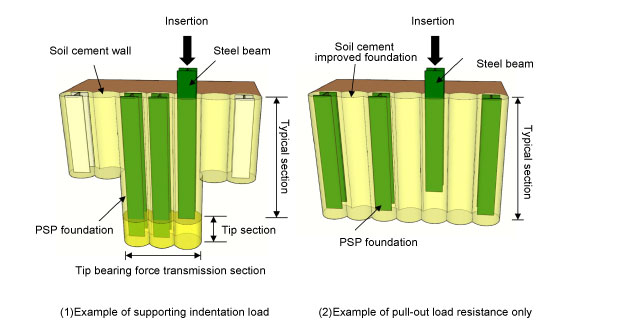
Figure 1 Conceptual layout of PSP II Method
(When PSP foundation is arranged at the position of the earth retaining wall)
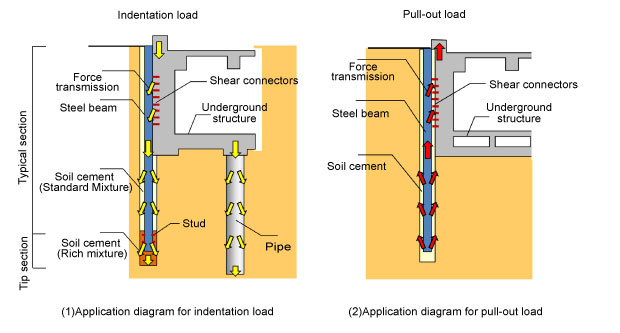
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of load transmission

Picture 1 Loading test to confirm structural performance
